3. Thixotropic fluids and water-based coatings In water-based coatings, such as the addition of bentonite with ion exchange capacity, a suitable electrolyte and an organic treatment agent, and careful mixing, the suspended particles can be negatively charged. In this way, not only the particles have the same electric charge, but also repel each other, are not easy to coalesce and sink, so that the coating has good suspension stability, and the coating can have thixotropic characteristics. (to be continued) Previous page Wenzhou Shenwei Hardware Co.,Ltd , https://www.cn-shwshw.com
Thixotropic fluids also have significant shear thinning properties, but are significantly different from pseudoplastic fluids. Not only the shear rate increases, but also the viscosity decreases. Under the condition that the shear rate is constant, the viscosity will gradually decrease with the extension of the shearing action time, and will become constant after reaching a certain limit value. After the shearing is stopped, the viscosity does not recover as immediately as the pseudoplastic fluid, and it takes a while to recover gradually. Therefore, the rheological properties of thixotropic fluids are time-dependent and cannot be described by shear rate-shear stress binary coordinates. Shear rate-shear stress-action time ternary coordinates must be used.
The situation in which the viscosity of the thixotropic fluid changes due to shear conditions is shown in FIG. 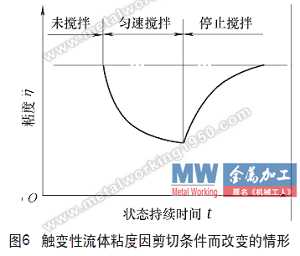
Water-based paint with thixotropic characteristics, which has the characteristics of shear thinning, is easy to apply, and it takes a certain time to recover the viscosity after application. Most of the brush marks and flow marks can disappear on their own, which is very good. Leveling.
4. Detection of rheological properties of coatings
Accurate determination of the rheological properties of a fluid is very difficult. For cast coatings, they can be tested in a simple way to give a rough idea of ​​their rheological properties.
(1) The shear thinning characteristic of the test coating is measured by a rotary viscometer with the same rotor, and the viscosity of the same paint is measured at different rotational speeds (eg, 6 r/min, 12 r/min, 30 r/min).
If the measured viscosities are the same at different speeds, the coating has no shear thinning characteristics.
If the viscosity measured at high speed is low and the viscosity measured at low speed is high, the coating has shear thinning characteristics. From the ratio of the viscosity value at the lowest rotation speed to the viscosity value at the highest rotation speed, the strength of the shear thinning characteristics of the paint can be known.
(2) Time-correlation of detecting viscosity change of paint If the viscosity is decreased with the stirring time at constant stirring, until a certain limit value is reached, or after sufficient stirring, the viscosity increases with the extension of the standing time (see Figure 6), it can be determined that it has a time correlation.
Since it is difficult to obtain stable data by measuring the viscosity of the coating with a rotational viscometer under uniform stirring conditions, it is not easy to determine the left half of the graph of Fig. 6. However, it is feasible to measure the viscosity of the paint after it has been thoroughly stirred, and the right half of Figure 6 is measured.
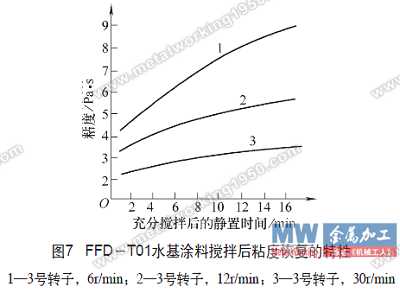
The method used by the author in the laboratory is: after a sufficient amount of paint is placed in a high-speed mixer for 10 minutes, the paint is placed in a plurality of small beakers, and then a cup of paint is taken every time, and the viscosity is measured by a rotational viscometer. And plotting the viscosity as it changes with the rest time, it is easy to judge whether the rheological properties are time-dependent and the thixotropy. Figure 7 is a measurement of the FFD-T01 water-based paint developed by the author.