General smelting process: Some explanations in the smelting process of aluminum alloys. Frequently used hexachloroethane (C2CI refined, using a bell jar, such as a counter-collapser) The use of different refining agents has different effects and the scope of application is not the same. Comparison of commonly used refining methods is shown in Table 6-6. (4) Pouring.For the general requirements of the casting, after the inspection of the gas content, it can be poured.When casting, depending on the thickness of the casting and the temperature of the aluminum liquid, the pouring speed is controlled separately. Pour, wait until the liquid flow is steady, quickly pour, Prepare the charge before smelting. 1 According to the bill of materials, take the charge. 2 Remove grease, rust and other dirt from the charge. 3\A1. Co is warmed up according to the following requirements, see Table 6-9 2 Prepare and pre-heat the refiner, covering agent and refining agent, and clean the citrus vortex, ingot mold and melting tool. The graphite orange pod can be made from the old graphite vortex and should be preheated to 200-.300 tons before use. S.S Braided Hose,Water Tap Hose,Flexible Braided Hose,Stainless Steel Braid Hose kaiping aida sanitary ware technology co.,ltd , https://www.aidafaucet.com
1 According to the alloy grades specified in the casting technical requirements, the chemical composition range of the alloy can be found out and the chemical composition can be selected from it;
2 According to the element's burning rate and composition requirements, calculate the ingredients, get the charge of various charge materials, and select the charge. If the charge is contaminated, it needs to be treated.
Ensure that all charge materials are clean, free from rust, and warm up before feeding;
3 Inspect and prepare for melting of appliances, paint, and preheating to prevent contamination of gases, inclusions, and harmful elements;
4 feeding, the general feeding sequence is the return charge, the intermediate alloy and the metal material, the low melting point easily oxidized metal material, such as magnesium, is added after the charge is melted;
5 In order to reduce the suction and oxidation pollution of the alloy liquid, it should be melted as soon as possible to prevent overheating. If necessary, some alloy liquids must be covered with a covering agent;
6 After the charge material is melted, refining treatment is carried out to purify the alloy liquid and test the refining effect;
7 According to the need to be modified and subdivided tissue processing to improve performance, and test the treatment effect;
8 adjust the temperature, casting, some alloys should be stirred before pouring, in order to prevent the occurrence of specific gravity segregation.
The purpose of alloy smelting is to obtain a molten metal that meets the requirements. Different types of metals require different smelting methods and equipment. Such as the melting of steel is the use of converters,
Open hearth furnaces, electric arc furnaces, induction furnaces, etc.; cast irons are mostly cupola furnaces; non-ferrous metals such as aluminum alloys, copper alloys, etc. are fused using the Komatsu A furnace.
First, the smelting of aluminum alloy Cast aluminum is one of the most widely used casting non-ferrous alloys in industrial production. Because the melting point of the alloy is low, it is easy to oxidize and suck during smelting. The low-boiling elements æž·Mg and Zn in the alloy are easily evaporated and burned. Therefore, the smelting of the aluminum alloy should be carried out in isolation from the fuel and gas.
1. Aluminum alloy smelting equipment Aluminum alloy smelting is generally carried out in orange IP, depending on the heat source used.
There are different types of coke heating furnaces, electric heating mandarins, etc., as shown in Figure 6-1.
The commonly used address vortex are graphite vortex and iron citrus worm. The mandarin orange is mixed with fire-resistant material and graphite and burned. Iron site vortex is cast from cast iron or cast steel and can be used for melting of low melting alloys such as aluminum alloys.
2. Smelting of aluminum alloys The smelting process of aluminum alloys is shown in Figure 6-2. 
1 Calculate and prepare ingredients according to brand requirements. According to practical experience, based on the calculation of the quality of the ingots (because the aluminum ingots are not good for sawing and learning, and then go back to other chemical components. If the new materials account for most of the ingredients, they can be based on the chemical composition of the upper limit, generally minus It can still meet the standard after burning.
Note: All charge materials must be dried before being put into the site A, especially in a climate with high humidity, so as not to have large gas content in the aluminum liquid, even if it is difficult to remove the gas through the degassing process.
After the empty mandarin oranges were preheated to dark red, the metal coating material and the covering agent added after drying seemed to cover the surface of the aluminum liquid just after melting, and quickly heated up and melted. After the molten aluminum begins to melt, it must stop the blast and observe it when exposed to direct sunlight. If the surface of the molten aluminum is slightly dark red and the gait is 680-720, you can degas.
3 refining. Refining agents commonly used for smelting aluminum alloys, see Table 6-4
Press into C2C16 with a total charge of 0.2%-0.3% (preferably pressed into a block crucible, with bell jar pressed at a depth of 100-150mm from the bottom of the pot, and move horizontally slowly, this time due to C2C16
The following reaction occurs with the aluminum liquid:
3C2C16+2A1 A 2A1C13åž+3C2C14 reacts to form a large number of bubbles and brings H: and A1203 inclusions in the aluminum liquid to the liquid surface.
The alloy is purified. Pay attention to use should be well ventilated, because C2C16 preheat decomposition
C12 and C2C1; are strongly irritating gases. Remove slag immediately after degassing and leave it still
5 to 10 minutes.
Then check the gas content of the Ming solution. Use a small spatula to dip a small amount of liquid aluminum. After a few moments of cooling, use a scrap saw blade to move the liquid. If there are no air bubbles protruding from the needle tip, then the degassing effect is proved to be good. For a large number of bubbles, a degassing operation should be performed again.
For the casting of aluminum alloy refining agent hexachloroethane (C2CQ, adding appropriate additives can delay the reaction speed to improve the refining effect. The composition and configuration method of hexachloroethane refining 411 containing additives are shown in Table 6-5. 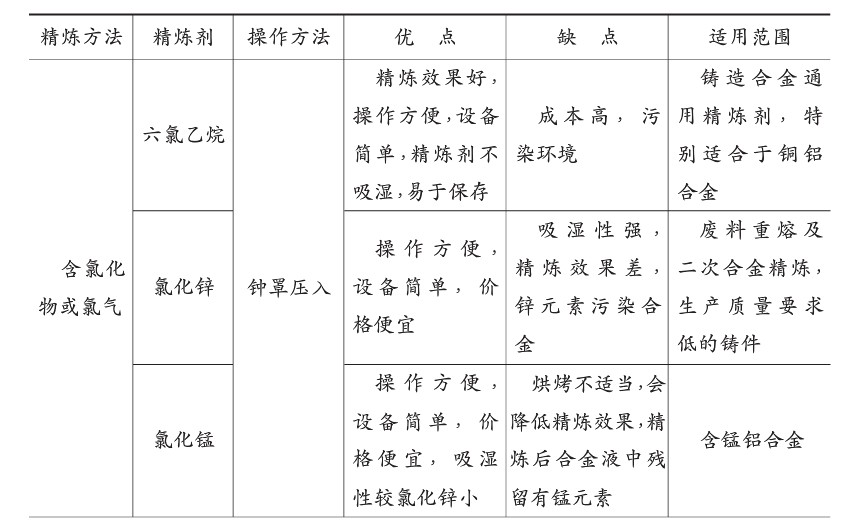
See the alloy liquid rose to the riser neck after pouring slower to enhance the feeder feeding capacity. In the case of castings with cores, flaming at the vents with a flame when the molten aluminum is about to be poured can reduce or avoid the “bonfire†phenomenon and the chance of the core gas entering the casting.
5 deterioration. Castings that require increased mechanical properties should also be refined after
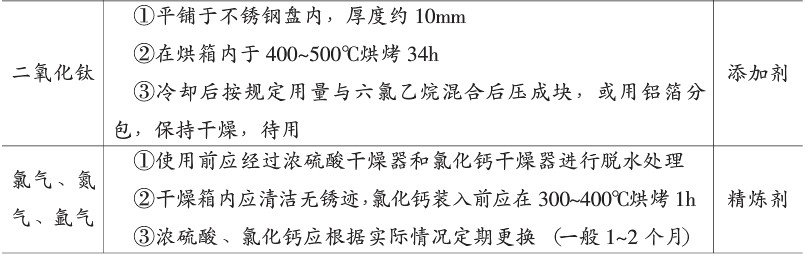
At 730-750°C, a bell jar was used to press in a 1%-2% modifier for the total charge. The commonly used modificator formulations are as follows: Preparation of NaC135% + NaF65% aluminum alloy smelting modifier and refining agent is shown in Table 6-7. 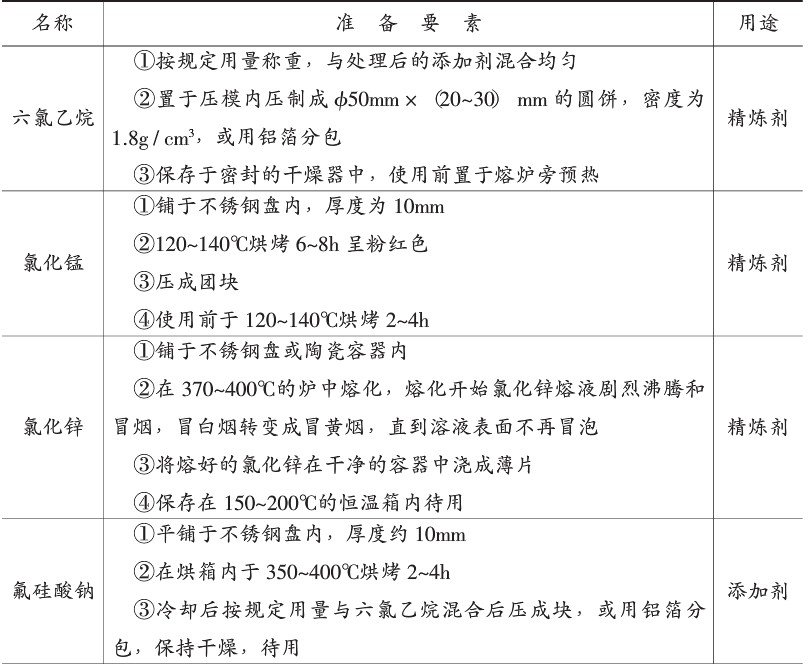
 6
6
contact),
The main measures for obtaining high-quality aluminum liquids are: sequestration of gas and furnace gas, degassing, slag removal, mixing as little as possible, and strict control of the process.
Second, the melting of the intermediate alloy in the melting of aluminum alloys, usually by adding the method of adding alloy alloy elements, which can reduce the burning loss, increase production efficiency and reduce production costs. The melting process specifications of the master alloys are similar. Here only the melting of Al-Co master alloys is taken as an example.
1. Ingredient preparation composition is Co5%+A195%, raw material specification is shown in Table 6-8 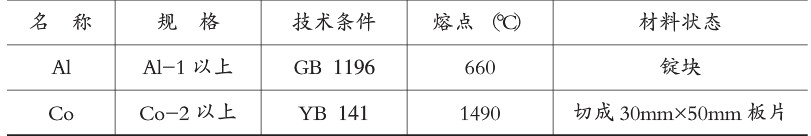

3. Melting 1 Add an aluminum ingot for melting.
After the second is completely melted, remove slag.
3 uniformly spread a layer of 80% glass powder + 20% borax on the molten metal surface, and then rise to 900-10000C.
4 Add the batch batches directly to the inscription and stir well with a graphite rod. Each batch should be fully stirred, and then the batch should be added after the previous batch has completely melted.
5 Cool down to 800-8200C, refine with 0.2%-0.3% of hexachloroethane.
6 The slag removal and pouring into ingots with a thickness of no more than 6 mm.
Note: 1 Each time the metal is pumped, use a graphite rod to stir 1-2min; 2 Select one sample before and after pouring, send the number and serial number, and send it to the laboratory for analysis of chemical composition.
4. Inspection items Inspection items include:
1 Chemical composition requirement C. The content is 4%-6%;
2 Ingot thickness ≤15mm;
3 Surface conditions and fracture requirements: 1 The surface and fracture should be no large slag inclusions or large pieces of small slag inclusions; 2 fractures should be no pinholes visible to the naked eye, the crystal structure should be dense,
No significant color difference. If the above requirements are not met or other problems arise, remelting shall be carried out or the inspector and the technologist shall negotiate with each other.
Third, improve the quality of aluminum alloy smelting
1. "Defend", "Row", and "Dissolve"
The general rules of nitrogen uptake and denitrification in aluminum liquids, the interdependence between nitrogen and oxidized inclusions were discussed in the foregoing. The commonly used refining processes were introduced, and the conditions of primary pores formed by aluminum castings were analyzed. We can conclude that we can eliminate them. The pores, the removal of oxide inclusions, and the reduction of the scrap rate of aluminum castings are summarized as "defense." row"
"Solution" 3 words.
“Prevention†means that water vapor and gas-containing contaminants are mixed into the aluminum liquid to reduce the original nitrogen content of the original solution before solidification.
"Row" is to remove oxygen inclusions and gases through refining, remembering that "slag removal is the basis of degassing and reducing the original content of hydrogen in the inscription.
. "Solubility" is the use of rapid solidification, or to increase the crystallization pressure during solidification, that is, to increase the crystal growth rate, so that all nitrogen in the aluminum solution is solid-dissolved in the aluminum casting without formation of pores.
Arrange and select the three prevention and treatment technologies for "prevention," "discharge," and "dissolve," and follow the principle of "prevention first."
Production practice has proved that the most effective refining method can usually only improve the pinhole grade of the casting by 1-2 grades, but if you do not pay attention to it, the purity of the aluminum liquid will be greatly reduced.
It is also difficult to completely remove gases and oxide inclusions using the best refining processes.
The effect of “solubility†is obvious. When using metal type, graphite type, low pressure casting, back pressure casting, squeeze casting, and die casting, the requirement for the purity of the Ming solution can be appropriately relaxed.
Correctly apply the "defense", "discharge" and "dissolve" three sets of processes, strictly follow the principle of "prevention first", and must implement the specific smelting and casting process operations. Only the basic smelting operation is excellent enough to fully and correctly implement These principles. The basic operations of the smelting operation include: preparation and careful handling of smelting equipment, smelting tools, refining agents, modificators, careful premelting and drying of the covering agents, proper agitation, slag removal operations, and careful pouring.
2. The generation of air hole defects A variety of defects will occur in the production of alloy castings. The air hole defects are defects that often occur in sand casting and are important issues affecting the quality of aluminum castings. Pore ​​defects often occur in the thick parts of large castings, as well as in the riser roots and machining end faces of small and medium sized aluminum castings. The generation of pores is related to the moisture and gas permeability of the sand, and also relates to the smelting quality of the alloy and the raw material of the alloy.
In the pouring process, there are four aspects of the source of the generated or evolved gas.
1 Molten metal precipitated gas, because the gas in the smelting process mainly comes from various charge, furnace gas, lining, tools, flux and moisture in the surrounding atmosphere, N2'02'
H2' C02' CO' SO: Hydrocarbons produced by the combustion of organic matter, etc. When pouring,
It is also possible to absorb large amounts of H2, and when it cools, it continuously precipitates due to the decrease of its solubility.
2 Organic matter in the core is decomposed at high temperatures to produce gas.
3 The mold releases gas at high temperatures, and the wet gas releases more.)
Because sand is usually composed of sand and drilling agent. Sand is a material that is resistant to high temperatures.
Is the main body of sand, the most widely used private agent is the private soil, the private soil in the liquid metal under the thermal effect of the crystallization of water will be decomposed. Sometimes to meet certain performance requirements,
Other modeling materials such as pulverized coal, sawdust, etc. are added to the sand. These additives will generate gas at high temperatures. In addition, there are: (1) Alloy elements react with the water vapor of the mold to produce nitrogen at high temperatures: mX+nH2O->XrO+ nH2;2 Carbon and organic matter in the molding material are combusted to generate CO and CO: gas; decomposition of sand component, such as decomposition of limestone sand: CaCO3 -> CaO + CO2; urea in resin sand, urotropine "(CHz) 6N}
At high temperatures, NH3 is first decomposed and then decomposed; in addition, the decomposition of alkanes CH2+2--*nC+ i+ 1) H2
Gas in the 4 cavity. Large castings require more liquid metal during the pouring process. Generally, there are mud cores and more gas is released from the casting mold. Therefore, it is suitable to use bleed air. Moreover, hydrogen content accounted for 30% -40% of the contained gas content, and the rest was N2. 02
And CO, etc., while H: is derived from the atmosphere, and the moisture in various metal raw materials, fluxes, and coatings is thermally decomposed and occurs under high temperature conditions. H must be = 2H++02-reaction, which is a reversible reaction and decomposes 02_ easy to generate higher melting point with liquid metal
A12O3, the reaction equation is: 2A13+ +302- = A1203, which promotes the decomposition of water vapor, H + will continue to spread to the alloy liquid. Nitrogen exists in aluminum in two ways: The first is dissolved in the solution of atoms in the molten aluminum, called dissolved type, accounting for about 90%; the second nitrogen is adsorbed to the inclusions in the form of bubbles in the molecular state. Surface or gap, called adsorption type. Since the solubility of nitrogen in the aluminum alloy melt increases with temperature, as shown in Fig. 6-3, the alloy liquid absorbs a large amount of nitrogen during the smelting process. In the process of solidification of the crystals, since the temperature lowers the solidification of the surface layer first and the privateness of the alloy increases, although the decrease in the solubility of nitrogen needs to be precipitated from the molten metal, it has been difficult to retain the pores in the molten alloy. defect.
The longer the melting and holding time, the higher the hydrogen content. 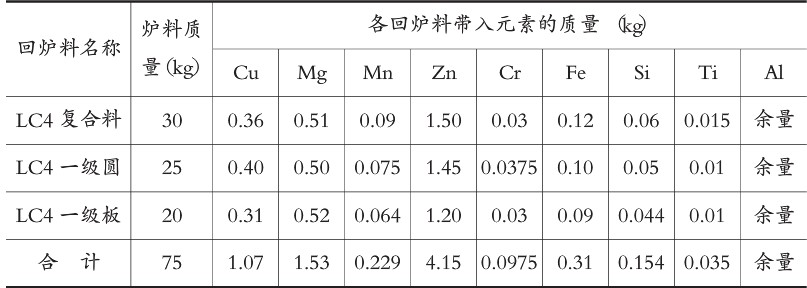
Figure 6-3 Hydrogen solubility in aluminum alloy melt at different temperatures (top illustration)
The solubility of nitrogen in the alloy liquid is proportional to the temperature, and is proportional to the pressure and the humidity of the air, that is, the nitrogen partial pressure.
The alloying elements and their contents also have a certain influence on the solubility. When the Si.Cu content increases, the solubility of nitrogen decreases. When the Mg content increases, the solubility of hydrogen increases. Different alloy composition, the critical content of hydrogen in the alloy liquid is also different, ZL104 aluminum alloy is hypoeutectic
Al-Si alloy has the largest amount of hydrogen absorption.
3. Measures to prevent blowhole defects To prevent the occurrence of blowhole defects in aluminum alloy castings in sand casting, effective measures must be taken to minimize the moisture content of the raw materials, strengthen the smelting quality management, reasonably select the casting process, and increase the mold's exhaust capacity. Specifically there are the following aspects.
1 All raw materials and smelting tools should carefully remove rust, oil, slag, etc. on the surface. The quality of the intermediate alloy and recycled material should also be well controlled. Poor quality recycled materials such as broken metal swarf and pouring risers should not be used in large quantities. . Metal raw materials, modifiers,
Refining agents, ladle, stirring spoons, etc. should be dried before use, while J# A should be preheated until dark red can be added to the melt. In addition to condensed water on the surface of the metal, there is also crystal water formed by the action of the metal oxide film. At a low temperature of 200-300°C, only some of the condensed water and dissolved water can be removed, and it is relatively easy to remove most of the condensed water only at a temperature above 500°C. Crystal water.
2 The smelting time should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the inspiratory capacity of the alloy. Smelting temperature should not be too high, the higher the temperature, the greater the amount of suction, generally does not exceed 8000C melting process temperature measurement device control. It is also necessary to control the metamorphic time. The longer the metamorphic time, the higher the metamorphic temperature, and the more severe the oxidation and inhalation. Since the oxide film on the aluminum alloy surface has a protective effect, it can prevent the molten metal from directly reacting with moisture in the atmosphere. During the smelting and pouring process, it is necessary to avoid the destruction of the oxide film on the liquid surface as much as possible. During refining and deterioration, the stirring spoon stirs smoothly under the liquid surface. In particular, the refining operation should be carefully performed, and the refining process is an important part of preventing the blowholes. The molten metal should be poured smoothly with uniform speed, and the minimum vertical distance between the ladle and the cast should be maintained.
3 Control sand permeability. The high air permeability of the sand type makes it easy for the metal liquid to infiltrate between the sand grains to form a mechanical sand, as well as defects such as large surface roughness and poor size of the casting. If the air permeability is too low, the porosity defect tends to be large. The sand of the general sand type should have small air permeability and low surface hardness, while the back sand should have higher air permeability, and the hardness should be higher in order to carry it, which helps to ensure the overall air permeability of the mold. Without the collapse of the box, the sand permeability is generally 80-100.
Also strictly control the moisture content in the sand, generally controlled at 4%-5%. The sand type has a high moisture content and the pore defects are worsened. When the cavity is repaired, do not brush too much water. The pouring site should not be sprinkled, and keeping air dry is a problem that cannot be ignored.
(4) Air holes in the sand mold. In the sand type of the upper and lower type should be vented,
To increase the gas discharge during the pouring process. The top of the stomata should have a certain distance from the wall, usually 4 to 6 mm, and the distance is too large to be detrimental to the exhaust. The exhaust of the lower part of a large casting is more important. In addition to the gas hole, the casting sand can also be used to increase the height of the casting. same,
The sand should also be kept clean, and the impurities in the sand and raw sand should be cleaned in time.
5 enhanced sand core exhaust capacity. Large and complex aluminum alloy castings are inevitably subject to sand cores. Since the agent in the sand core will generate a certain amount of gas when poured at a high temperature, it is necessary to try to discharge. The common method is to set the exhaust path in the sand core, Li Fang wax line, air hole, etc. The larger volume sand core can fill slag or coke block, these measures are very effective. In the core of the sand core should be fitted with a vent vent, if the core of the sand core and the sand gap, can be used to block the molten metal asbestos rope to prevent the liquid metal blocking the exhaust hole.
Large complex aluminum castings should also be ignited at the exit of the exhaust system when pouring.
In order to reduce the pressure of discharge, it contributes to the emission of gas.
The amount of self-binding agents and additives in the sand core should be reasonable. The amount of gas generated by the self-bonding agent is generally large, and the amount of addition should be minimized under the premise of ensuring the performance of the sand core. For tung oil sand core, the mass ratio of tung oil added is generally 2%-3%. In order to increase the wet strength and surface hardness of the sand core, the amount of dextrin added is generally 1% to 2% of the dextrin gas. Therefore, the amount of dextrin to be added is strictly controlled. In addition, the sand core should be baked for a long time before use, and it can be placed in the mold after cooling.
6 enhanced cold iron exhaust. To form a sequential solidification, some castings will place cold iron to increase the rate of condensation while cold irons will have less exhaust. To improve the exhaustability of cold iron,
The vent can be pulled on cold iron and coated with fire-resistant paint.